Step 3: Consider your integration and customisation needs
Your CRM should integrate seamlessly with the tools you already use. Integrations ensure data flows smoothly across your business, creating a single source of truth and improving efficiency. Common integrations include:
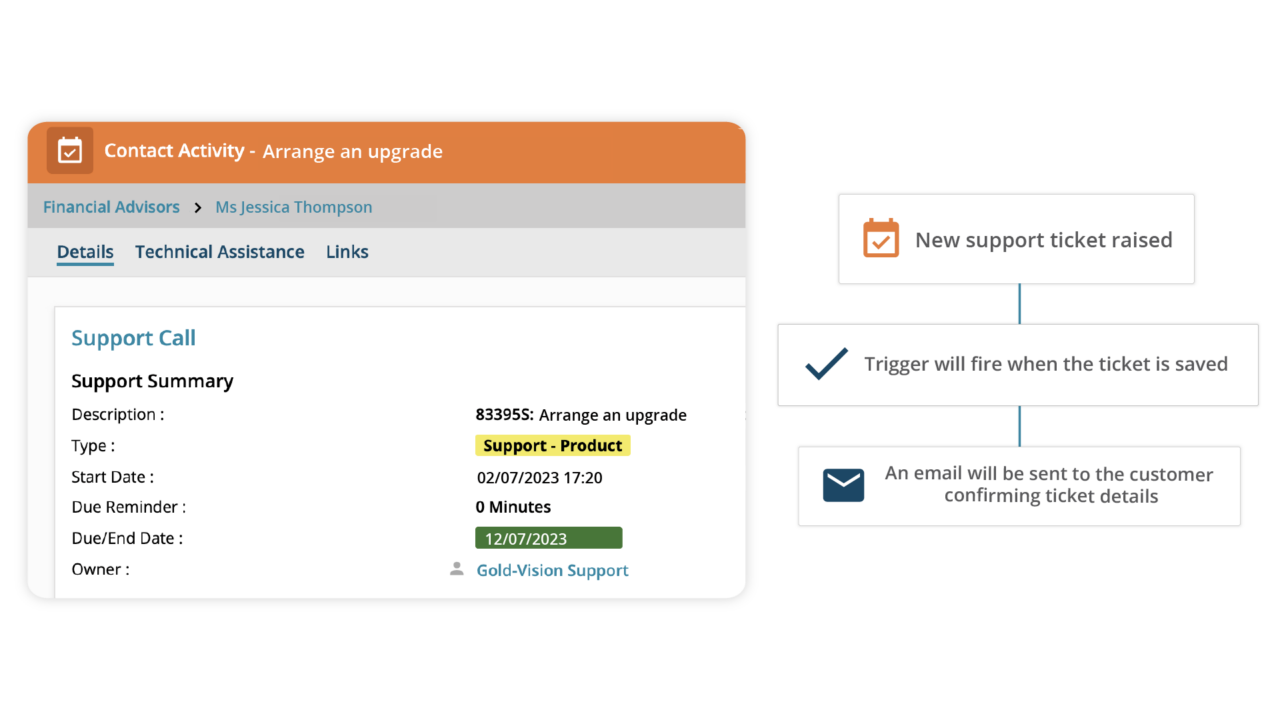
- Email (Gmail, Outlook) – Automatically log emails, so your sales and support teams can see the full customer conversation history without switching between platforms.
- Accounting software (QuickBooks, Xero) – Sync invoices, payments, and financial data to give sales teams visibility into customer accounts and outstanding payments.
- Document management (Adobe Sign, SharePoint) – Store and access contracts, proposals, and key documents directly from your CRM to speed up approvals and collaboration.
- ERP and inventory management systems (Sage, Dynamics) – Connect stock levels, order history, and financial data, so sales teams can provide accurate quotes and delivery timelines.
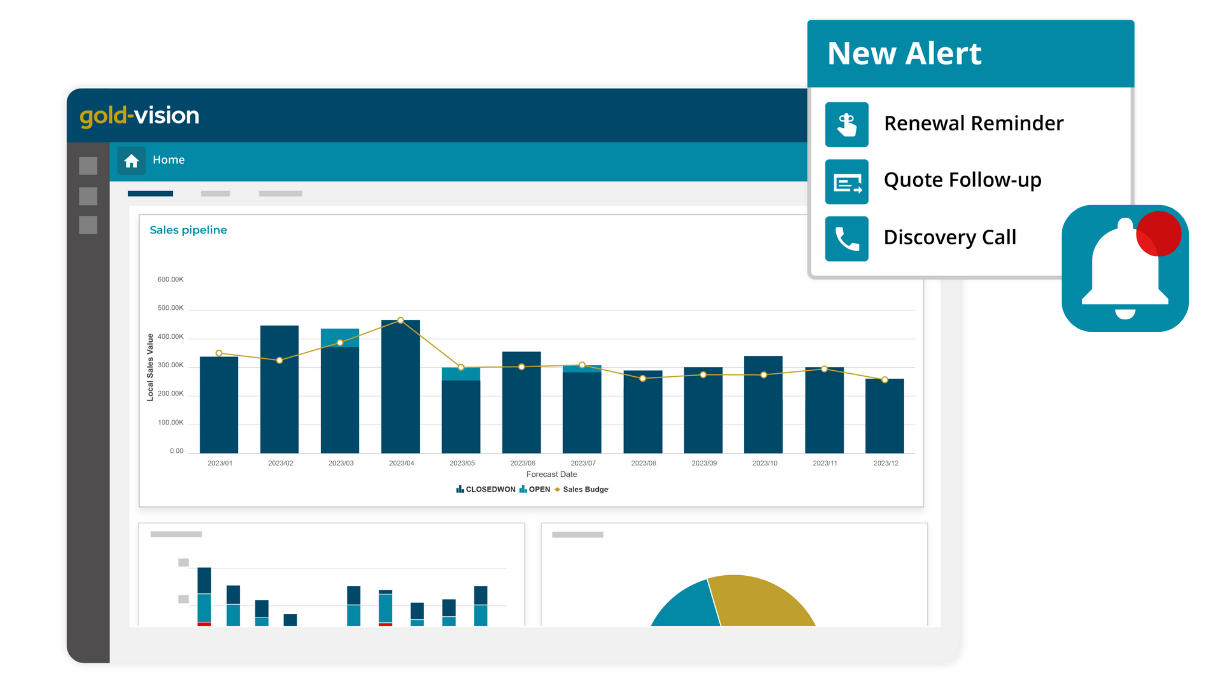
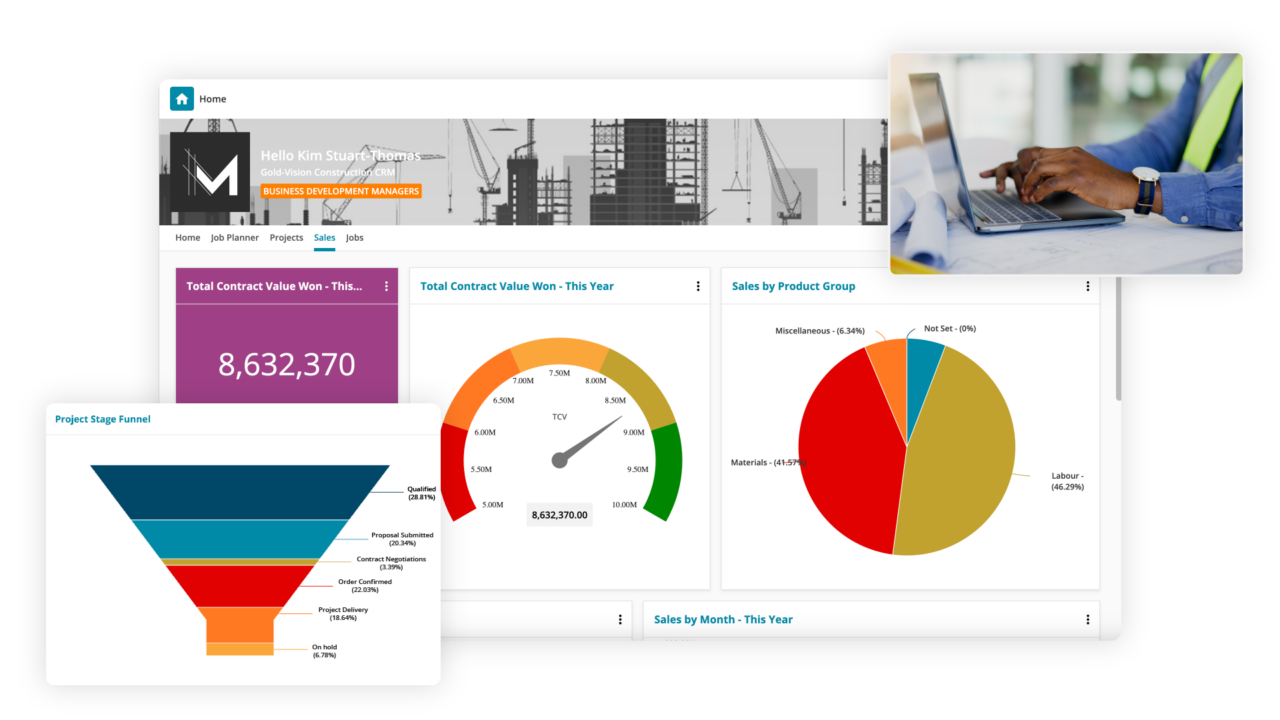
These integrations allow for accurate reporting, giving you a complete picture of customer interactions, finances, and sales performance—all in one place.
Additionally, consider how customisable the CRM is. Can you add custom fields? Modify screens and workflows? Does it have multi-language or currency features? These factors can make a big difference in long-term usability, especially as your business grows.